In corporate responsibility, the integration of NLP in CSRD/ESG reporting is emerging as a transformative approach. This article explores the multifaceted applications of NLP, shedding light on its potential to navigate the complexities of ESG data, enhance reporting efficiency, and contribute to more comprehensive and accurate sustainability reports.
From data identification and collection to processing, enrichment, and report creation, we dive into the ways NLP can be harnessed to address the challenges and opportunities inherent in CSRD/ESG reporting. And as we navigate through the diverse applications of NLP, we will also address the ethical considerations, limitations, and future directions of this technology in the sustainable reporting domain. The journey ahead illuminates the possibilities and challenges, offering insights and recommendations for companies seeking to leverage AI to transform the future of business.
First Thing First: Definitions and Context
What is ESG/CSRD Reporting?
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting, recently enhanced by the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) in the European Union, is a framework for companies to disclose their impact and practices related to environmental conservation, social responsibility, and governance structures. The importance of complying with this directive stems from the increasing emphasis on corporate responsibility and sustainability, with stakeholders, investors, and consumers demanding greater transparency and accountability from companies.
The journey towards effective CSRD/ESG reporting presents both challenges and opportunities for companies. Challenges include ensuring data availability, maintaining data quality, achieving standardization, and enhancing comparability and analysis across different companies and sectors. However, overcoming these challenges opens up opportunities for companies to improve their sustainability practices, enhance their reputation, attract investment, and drive long-term value creation, within our planet’s boundaries.
What is NLP?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on the interaction between computers and humans through natural language. It enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language, thereby facilitating more intuitive and meaningful interactions. The evolution of this Machine Learning (ML) technique has been marked by the introduction of training methods, the transformers architecture, the scalability of models through improvements in processing (e.g. GPUs), and, more recently, the advent of Generative AI applications.
NLP, particularly with advancements like Large Language Models (LLMs) and Data-centric AI, faces its own set of challenges and opportunities. The challenges revolve around ensuring the ethical use of technology, managing data privacy, mitigating biases, and preventing potential mistakes and hallucinations in language models. However, the opportunities are vast, including automating content creation, enhancing customer interactions, extracting insights from unstructured data, and more.
Bridging ESG Reporting and NLP
In conclusion, the convergence of ESG reporting and NLP can be a game-changer for small and medium-sized companies. NLP, with its ability to analyze, interpret, and generate human language, can help companies navigate the complexities of CSRD/ESG reporting by automating data extraction, enhancing report quality, and providing insights for better sustainability practices.
Let’s explore each of these NLP techniques in detail.
NLP for ESG Data Identification
The Challenge: Diverse and Scattered ESG Data
In the realm of ESG reporting, companies grapple with the challenge of diverse and scattered data sources. ESG data can be hidden in a myriad of formats, scattered across various assets, both digital and physical, necessitating a sophisticated approach for accurate identification and extraction.
The Solution: NLP’s Advanced Capabilities
NLP emerges as a transformative solution, capable of scanning a multitude of information sources such as company documents, websites, news articles, and social media posts. It delves into the vast sea of unstructured text, pinpointing key themes, topics, metrics, and indicators essential for comprehensive ESG reporting.
Innovative Models and Techniques
- Semantic Search Model: Our team has developed a semantic search model that can sift through over 12,000 existing ESG metrics, aiding companies in finding the most relevant metrics for specific search topics.
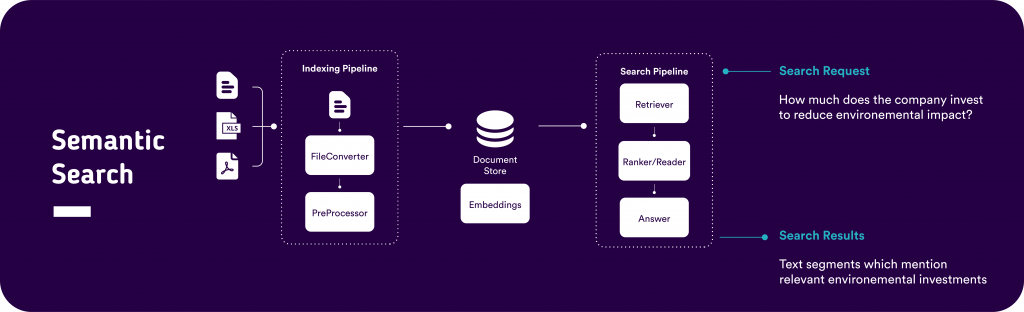
- ESGBert: Another innovation is ESGBert, a model adept at classifying text segments based on their relevance to distinct ESG subtopics, providing a granular and nuanced view of ESG data.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): NLP utilizes NER to identify entities like companies, numbers, dates, and measurements within the text, enriching the ESG data pool.
- Topic Modeling and Sentiment Analysis: These techniques are employed to gauge the sentiment and thematic context of the content, offering deeper and more insightful perspectives into the ESG landscape.
Aligning with Regulatory Standards
NLP plays a pivotal role in aligning companies’ ESG data with the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS). By mapping identified data to these standards and considering the double materiality perspective, companies ensure their reporting is both comprehensive and compliant.
In short: NLP – A Valuable Tool for ESG Data Identification
In addressing the challenges associated with diverse and scattered ESG data, NLP proves to be a valuable tool. It offers significant capabilities to aid companies in navigating the complexities of ESG data identification. By leveraging AI, companies can enhance their ability to align with regulatory standards and make strides toward fostering a more sustainable and responsible business ecosystem. The integration of NLP in ESG reporting is a step forward, but it is essential for companies to continue exploring and adopting a multifaceted approach – meeting the evolving demands of sustainability and compliance.
NLP for ESG Data Collection
The Challenge: Varied Sources and Formats
In the pursuit of comprehensive ESG reporting, companies are often confronted with the task of collecting and aggregating data from a wide array of sources and formats, such as PDFs, HTMLs, CSVs, etc. The diversity in data types and the sheer volume of information necessitate efficient and accurate techniques for data collection.
The Solution: NLP Diverse Techniques
NLP offers a suite of techniques, including web scraping, document parsing, and data extraction, to facilitate the collection and aggregation of ESG data from various sources and formats. AI not only aids in accessing information but also ensures that the data integrated into the reporting is relevant and accurate.
Practical Applications and Expertise
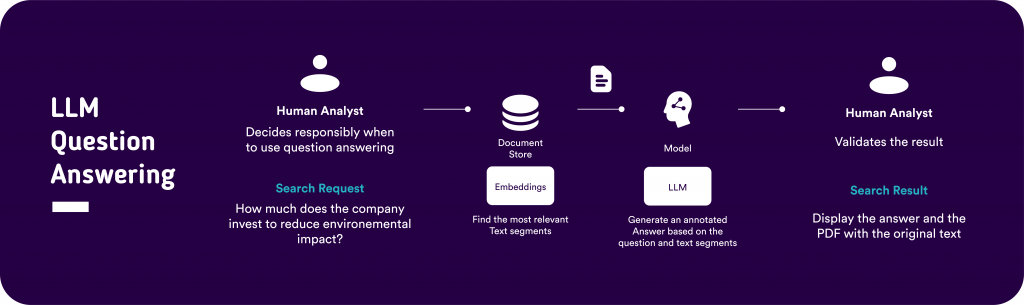
- Semantic Search and Question Answering System: We have developed a system that employs semantic search and question-answering to aid companies in finding and extracting ESG data from extensive documents, PDFs, email communications, and other written records.
- Standardized Data Aggregation: Our expertise extends to standardized data aggregation, enabling companies to amalgamate ESG data from diverse sources and formats into a unified and consistent representation, thereby enhancing the coherence and reliability of the reporting.
Ensuring Quality and Traceability
Maintaining the quality and traceability of ESG data is paramount in building credibility in ESG reporting and complying with regulatory standards. Embracing a hybrid approach that combines ML/AI with human expertise, particularly in scenarios demanding high data quality, can significantly enhance the validation, verification, and cleaning processes.
This human-in-the-loop system ensures that a human expert reviews and validates the results produced by the AI models, thereby fortifying the integrity of the data. Such an integration of technologies and human oversight fosters trust and reliability in the ESG reporting process, ensuring that the data not only meets regulatory standards but also upholds the highest quality benchmarks.

In short: NLP – Enhancing ESG Data Collection
While AI is not the sole solution, it serves as a valuable asset in the ESG data collection process. It offers companies the tools to efficiently access, integrate, and validate data from a multitude of sources and formats. By leveraging NLP, companies can enhance the quality and traceability of their ESG data, contributing to more accurate and credible reporting, and ultimately, advancing sustainability goals.
NLP for ESG Data Processing or Enrichment
The Challenge: Analyzing and Enhancing ESG Data
The task of analyzing and enhancing ESG data is a critical step in ESG reporting. It involves extracting meaningful insights from the collected data and presenting it in a manner that is both informative and accessible. The complexity and volume of ESG data requires sophisticated techniques for effective processing and enrichment.
The Solution: NLP’s Analytical Techniques
NLP offers a range of analytical techniques such as text summarization, text classification, sentiment analysis, and text clustering to analyze and enhance ESG data. These techniques enable companies to distill the essence of the data, categorize it effectively, gauge sentiment, and group similar data points, thereby optimizing the data for further research and processing.
Practical Applications and Innovations
- Text Summarization: We have leveraged NLP to summarize the main points and trends of ESG data, facilitating faster research and optimized processing.
- Sentence Embeddings: By converting text to sentence embeddings and storing them in a vector database, we have enabled fast and easy retrieval of relevant sentences based on semantic similarity.
- Sentiment Analysis: We have utilized NLP to observe the sentiment fluctuations regarding companies in news articles over time, providing an additional layer of insight into the public perception of ESG-related events and developments.
- Text Classification: NLP enables the classification of text segments into different ESG topics, such as climate change, human rights, diversity and inclusion, etc., facilitating easier filtering and analysis of relevant information.
In short: NLP – Elevating ESG Data Processing and Enrichment
NLP stands as a powerful tool in the realm of ESG data processing and enrichment. By employing a variety of analytical techniques, it enables companies to extract meaningful insights, optimize data accessibility, and enhance the overall quality of ESG reporting. Its integration in this phase is instrumental in advancing the depth and breadth of insights derived from ESG data, contributing to more informed decision-making and strategic planning for sustainability.
NLP for CSRD Report Creation
The Challenge: Crafting Comprehensive CSRD Reports
Creating CSRD reports is a meticulous task that demands precision, accuracy, and a comprehensive representation of a company’s ESG initiatives. The challenge lies in compiling vast amounts of ESG data into coherent, reliable, and informative reports that comply with regulatory standards.
The Solution: NLP’s Generative Capabilities
AI offers innovative solutions for crafting CSRD reports. It enables companies to leverage pre-trained models and existing reports to generate text fragments and suggestions, utilizing techniques such as natural language pre-training, fine-tuning, and generation. Importantly, NLP can integrate a human-in-the-loop approach, ensuring that the generated content is supervised and refined by human expertise.
Practical Applications and Innovations
- Pre-Training Data: We have scraped sustainability reports from over 2000 companies (2022), which serve as a rich source of pre-training data. This data is instrumental when creating a CSRD report, aiding in the report drafting process, and improving the whole model to perform all required tasks.
- LLMs for Natural Language Generation: Leveraging LLMs, we helped users in drafting answers or responses based on underlying ESG data. This application of NLP enhances the efficiency and coherence of the report creation process.

Ensuring Accuracy and Reliability
NLP also plays a vital role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of CSRD reports. By analyzing and refining the generated text, and by maintaining a humans-in-the-loop approach, it contributes to the creation of reports that are not only compliant with regulations but also reflective of the true ESG initiatives of the company.
In short: NLP – Aiding in the Creation of Reliable CSRD Reports
AI emerges as a valuable ally in the creation of CSRD reports. Its generative capabilities, coupled with human oversight, facilitate the crafting of comprehensive and accurate reports. By leveraging NLP, companies can streamline the report creation process, ensure compliance, and accurately represent their commitment to environmental, social, and governance principles.
Harnessing NLP for Enhanced CSRD/ESG Reporting
In this exploration of AI’s role in CSRD/ESG reporting, we’ve delved into its multifaceted applications, spanning from data identification to report creation. The potential of NLP is indisputable, especially when navigating the complexities and diversity of ESG data, offering a pathway to more coherent and comprehensive reporting.
- Key Findings: NLP stands as a pivotal tool, enhancing efficiency in data collection, providing deeper insights through data processing, and aiding in the crafting of accurate reports. Its applications are diverse, including text summarization, sentiment analysis, data validation, and natural language generation.
- Benefits and Advantages: The integration of NLP brings forth numerous benefits for companies, particularly in aligning with regulatory standards, ensuring data quality, and accurately representing sustainability initiatives.
- Recommendations for SMEs: Small and medium-sized companies are advised to start with specific applications, maintain human oversight, leverage pre-trained models, and prioritize data quality.
However, the journey with NLP is not without its challenges. Ethical considerations, data privacy, hallucinations (especially when using LLMs) and potential biases are hurdles to be addressed, necessitating a cautious and ethical approach to AI integration.
Looking forward, the horizon is ripe with opportunities for further research and development. The exploration of ethical AI, refinement of language models, and advancements in data quality management are just a few avenues that hold promise for elevating AI’s role.
The intersection of NLP and CSRD/ESG reporting holds significant promise. By embracing best practices, acknowledging limitations, and pursuing continuous innovation, companies can harness the capabilities of AI to contribute to a more sustainable responsible business future.
Read more on Sustainability:
Sustainability and Data Products – The perfect match?
How to Successfully Drive Your CSRD/ESG Initiative With a Data-driven Approach
Our Teams’ Double Impact at the SAS Hackathon 2023: Driving Sustainability with Data & Analytics
Read more on AI:
Navigating the EU AI Act: How Explainable AI Simplifies Regulatory Compliance
From Theory to Practice: A Generative AI Workshop to Guide a Leading Banking










