In this article, we will explore the exciting new features introduced in Spring Boot 3, the latest version of the popular Java framework. Spring Boot has revolutionized the way developers build Java applications by providing a streamlined and opinionated approach to application development. With each new release, Spring Boot continues to evolve and improve, empowering developers to create robust and scalable applications with ease.
Staying up-to-date with the latest versions guarantees access to new features, enhancements and security improvements, as well as community support, enabling developers to build high-quality applications efficiently.
Summary
1. Overview of Spring Boot 3
Spring Boot is a widely used framework for developing web applications and microservices in Java. It simplifies the development process by providing intelligent default configurations and eliminating repetitive tasks. Spring Boot accelerates application development by offering built-in features such as integrated application servers, dependency management and out-of-the-box support for many popular libraries and technologies.
Spring Boot 3 is a major release of the Spring Boot framework, released in November 2022. It includes several new features, improvements and bug fixes:
- Java 17 baseline: Spring Boot 3 requires Java 17 or higher. This means you can take advantage of the latest features and performance improvements that Java 17 offers.
- Support for generating native images with GraalVM: GraalVM is a high-performance virtual machine that can be used to generate native images of your Spring Boot applications. This can significantly improve the performance of your applications, especially on startup.
- Improved observability with Micrometer and Micrometer Tracing: Micrometer is a library that provides a unified API for collecting metrics from your Spring Boot applications. Micrometer Tracing is a library that provides tracing support for your Spring Boot applications. These libraries make it easier to monitor and troubleshoot your applications.
- Support for Jakarta EE 10 with an EE 9 baseline: Jakarta EE 10 is the latest version of the Jakarta EE specification. Spring Boot 3 includes support for Jakarta EE 10, so you can now use Spring Boot to develop applications that are compliant with the Jakarta EE 10 specification.
- Spring Framework 6: Spring Boot 3 is based on Spring Framework 6, so it includes all of the new features and improvements that were introduced in Spring Framework 6.
2. Enhancements
Spring Boot 3 introduces various performance enhancements and optimizations to boost application responsiveness and efficiency.
These improvements focus on reducing startup times, minimizing memory footprint, and optimizing resource utilization.
With a more streamlined and lightweight runtime environment, applications built on Spring Boot 3 will experience improved scalability and responsiveness, resulting in a better user experience and higher customer satisfaction.
We will mention one easy way to boost a spring boot application’s performance just below.
3. System requirements
Spring Boot 3 requires Java 17 (or above) and Spring Framework 6 (or above).
Build tools
Maven ➜ 3.5+
Gradle ➜ 7.x (7.5 or later)
Servlet containers
Spring Boot supports the following embedded servlet containers:
| Name | Servlet Version |
|---|---|
| Tomcat 10.0 | 5.0 |
| Jetty 11.0 | 5.1 |
| Undertow 2.2 (Jakarta EE 9 variant) | 5.0 |
GraalVM Native Images
Spring Boot applications can be converted into a Native Image using GraalVM 22.3 or above.
Images can be created using the native build tools Gradle/Maven plugins or the native-image tool provided by GraalVM. You can also create native images using the native-image Paketo build pack.
The following versions are supported:
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| GraalVM Community | 22.3 |
| Native Build Tools | 0.9.18 |
4. Compatibility and Migration
Migrating to Spring Boot 3 requires a series of associated migrations and dependency updates that must be carried out before upgrading to this latest version of Spring Boot. These include:
- Updating your organization’s applications, infrastructure, and CI/CD pipeline to use at least Java 17. The upside to this step is that it can be done before updating any of your Spring Boot applications.
- Any pre-existing Spring applications that utilize Java EE will require an update to Jakarta EE 9. While this may seem like a simple task of moving all imports from the Javax namespace to the Jakarta namespace, it also requires the migration of any third-party libraries to versions that are compatible with Jakarta EE 9.
There are instances when we may not need to refactor package names when upgrading our software, as some dependencies such as javax.sql.DataSource already belongs to JDK 17, not Jakarta EE. In these cases, it is not necessary to make any changes to the package name, as it is already consistent with the latest version of our app. It is important to note, however, that it is essential to thoroughly review and test all dependencies to ensure that they are compatible with the new version of the code.
Lastly, depending on which version of Spring Boot your applications are being migrated from, there may be a need to make several required changes to both the application’s code and configuration when moving to Spring Boot 3.
5. New Tools and Framework Integrations
5.1. Java 17 Baseline and Java 19 Support
The most important news we are concerned about is that Spring Boot 3 supports Java 17 at least.
If you are currently working with Java 8 or 11, you will need to migrate to JDK 17 before enjoying Spring Boot 3 application development.
Spring Boot 3 also works well and has been tested with JDK 19.
According to the Java Community and the experts:
- “Next Java long-term support release delivers thousands of updates, further improving the language and platform to help developers be more productive”
- “Oracle JDK 17 gives customers security, performance, and bug-fix updates through September 2019”
You might like to read about the new features available in JDK 17.
5.2 GraalVM Native Image Support
With Spring Boot 3, you can now use GraalVM native image support.
Spring Boot 3 applications can now be converted into GraalVM native images which can provide significant memory and startup-up performance improvements.
Say goodbye to your JVM And enjoy the major engineering effort undertaken across the entire Spring portfolio!
To get started with GraalVM native images, please visit the updated Spring Boot reference documentation.
5.3. Jakarta EE API
Spring Boot 3 has migrated from Java JEE to Jakarta JEE APIs for almost all dependencies.
The new compatible dependencies of Jakarta JEE are coming through Jakarta JEE 10, including :
- Jakarta Validation 3.0
- Jakarta Persistence 3.1
- Jakarta Servlet 6.0
- Jakarta Transaction 2.0
- Jakarta JSON 2.1
- Jakarta WS RS 3.1
- Jakarta XML WS 4.0
You might like to read about the Jakarta JEE 10 core profile.
5.4 Spring Framework 6
Spring Boot 3 builds on and requires Spring Framework 6. In this release, there are several Spring upgraded modules such as :
- Spring Security 6.0
- Spring Session 3.0
- Spring WS 4.0
- Spring Integration 6.0
- Spring Batch 5.0
- Spring Kafka 3.0
- Spring Data 2022.0
We should mention that Spring Framework 6 is now compatible with the JPA support for Hibernate ORM 6.1.
5.5 Web Flux Enhancements
Spring Framework 6 provides us with new enhancement in the WebFlux Spring Module for reactive programming :
- New PartEvent API to stream multipart form uploads (both on client and server).
- New ResponseEntityExceptionHandler to customize WebFlux exceptions Flux return values for non-streaming media types (no longer collected to List before written).
- Early support for Reactor Netty 2 based on Netty 5 alpha.
- JDK HttpClient integrated with WebClient.
You might like to read about the new WebFlux Spring module.
5.6 Micrometer Metrics & Tracing Updates
As we know, Micrometer is the metrics and tracing collection facade of a springboot application that uses Actuator.
SpringBoot 3 comes with two major updates introduced in Micrometer 1.10:
- Auto-configuration for Micrometer Observation API.
- Auto-configuration for Micometer Tracing.
So, SpringBoot 3 offers us the ObservationRegistry interface that can be implemented to create observation which provides a single API for both metrics and traces.
You might like to read about micrometer metrics and tracing with Actuator Spring Boot 3
5.7 Dependency upgrades
As discussed above, SpringBoot 3 depends on the Spring Framework 6 version at least so other dependencies are upgraded as follows:
- Kotlin 1.7 +
- Lombok 1.18.22+
- Gradle 7.3+
5.8 Miscellaneous
These are also some improvements and deprecations in SpringBoot 3.
Improvements:
- Auto-configuration for the new Elasticsearch Java Client has been introduced.
- Apache HTTP client a JdkClientHttpConnector will now be auto-configured
- The @SpringBootTest annotation can now use the main of any discovered @SpringBootConfiguration class if available. This means that tests can now pick up any custom SpringApplication configuration performed by your main method.
Depreciations:
- JsonMixinModule scanning-based constructor has been deprecated, and ClientHttpRequestFactorySupplier is replaced with ClientHttpRequestFactories.
- Cookie comment properties are now no longer supported.
- RestTemplateExchangeTagsProvider, WebClientExchangeTagsProvider, WebFluxTagsProvider, WebMvcTagsProvider, and related classes have been replaced with ObservationConvention equivalents.
- The no-args constructors on HealthContributor @Configuration base classes have been deprecated.
- DefaultTestExecutionListenersPostProcessor and SpringBootDependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener have been deprecated in favor of Spring Framework’s ApplicationContextFailureProcessor.
- The properties management.metrics.export.<product> are deprecated; the replacement is management.<product>.metrics.export.
- The push setting of management.prometheus.metrics.export.pushgateway.shutdown-operation in favor of post.
- Also, @AutoConfigureMetrics has been deprecated in favor of @AutoConfigureObservability.
6. Security Enhancements
In this section, we will discuss the security-related updates in Spring Boot 3.
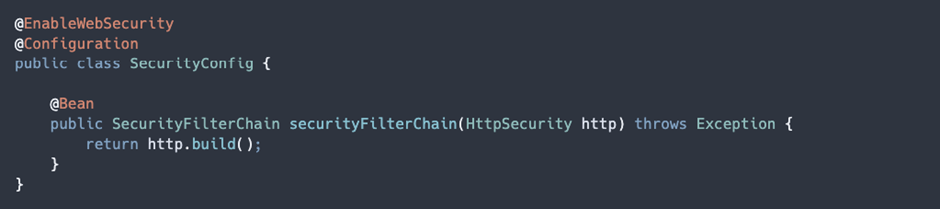
6.1 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter removed
In previous versions of Spring Security, When we wanted to configure the Security settings, we had to extend the WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter class.
This class has been deprecated and removed in Spring Security 6.
Instead, we should now take a more component-based approach and create a bean of type SecurityFilterChain.
Example:
6.2 authorizeHTTPRequests
Instead of using authorizeRequests, which has been deprecated, we should now use authorizeHttpRequests.
This method is part of the HttpSecurity configuration and allows you to configure fine-grained request matching for access control.
Example:
In this example, we allow access to the “/api/auth” request, while requiring authentication for all other requests.
6.3 requestMatchers replacing antMatchers, mvcMatchers & regexMatchers
In Spring Security 6, AntMatcher, MvcMatcher, and RegexMatcher have been depreciated and replaced by requestMatchers or securityMatchers for path-based access control. This allows us to match requests based on patterns or other criteria without relying on specific matchers.
In the previous example, we can see that the system permits access to the “/api/auth” endpoint without authentication while requiring authentication for all other requests.
7. Community and Ecosystem
Find below the respective links for:
- The platform for community contributions, bug reporting, and discussions
- The official docs hub of Spring Boot 3. It provides comprehensive documentation, guides, and tutorials to help developers get started and stay up-to-date with the latest releases of Spring Boot.
- The official Spring Boot forum is a community platform where developers can participate in discussions, seek help, and share their experiences.
- Stack Overflow: The Spring Boot tag on Stack Overflow is a community platform where developers can participate in discussions, seek help, and share their experiences.
- Spring Community Calendar: Check the Spring community calendar for scheduled events, including online webinars and conferences.
- SpringOne at VMware Explore Event in Las Vegas
Conclusion
Spring Boot 3 is a major release that introduces several new features and improvements, including:
- Support at least Java 17
- GraalVM native image support
- Improved observability with Micrometer and Micrometer Tracing
- Support for Jakarta EE 10
- Spring Framework 6
- Web Flux enhancements
- Micrometer metrics and tracing updates
- Dependency upgrades
- Miscellaneous changes and deprecations
These new features and improvements make Spring Boot 3 a more powerful and versatile framework for developing Java applications. They also make it easier to build applications that are more efficient, scalable, and secure.
If you are currently using Spring Boot, you should consider upgrading to Spring Boot 3 to take advantage of these new features and improvements. If you are new to Spring Boot, Spring Boot 3 is a great starting point for building your next Java application.
More Resources
To learn more about Spring Boot and how to implement & use Redis cache, you can take a look at our insights Redis Cache in Spring Boot applications or Distributed Caching using Redis in Spring Boot applications.
Read more Insights on Software Product Engineering.














